13. Uploading Files and Images¶
In traditionally rendered forms, the payload of files to be uploaded is submitted together with the form data. This approach is not very user friendly, because submitting such a form can take a considerable amount of time on slow Internet connections. Even worse, if the form does not validate on the server, that upload must be repeated again. Moreover, if a form contains more than one file to be uploaded, the maximum size a client can upload to the server must be shared for all of them [3], [4].
Therefore django-formset handles file uploads asynchronously. This means that the payload of a file is uploaded to the server as soon as the user opens the file dialog or drags a file on the area nearby the file input button. While the payload of that file is transferred, the user can fill out other fields. The uploaded file is stored in a temporary folder on the server. After successful file upload, a unique and signed handle is returned to the client. On form submission, this handle then is used to refer to the previously uploaded file inside the temporary folder. If the form validation passed successfully, that file then is moved to its final destination.
13.1. Example¶
A Django form accepting files for upload can be converted easily to django-formset’s asynchronous file uploads, simply by replacing the widget.
from django.forms import forms, fields
from formset.widgets import UploadedFileInput
class UploadForm(forms.Form):
avatar = fields.FileField(
label="Avatar",
widget=UploadedFileInput,
required=True,
)
Remember, the Django view accepting the form data, must inherit from
formset.views.FileUploadMixin. No extra endpoint is required to activate this feature.
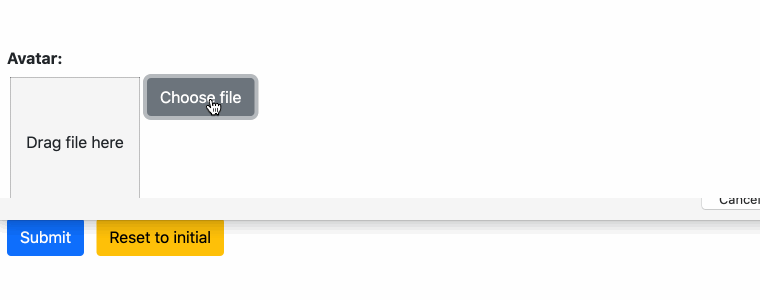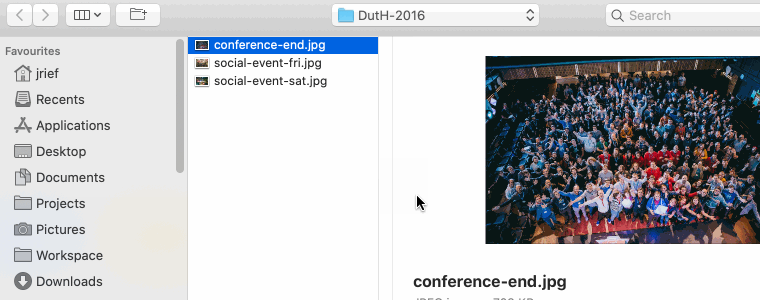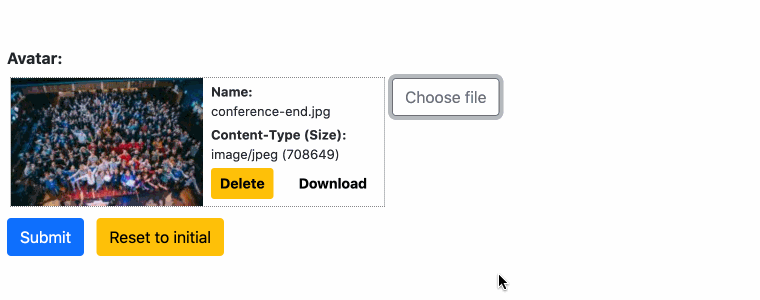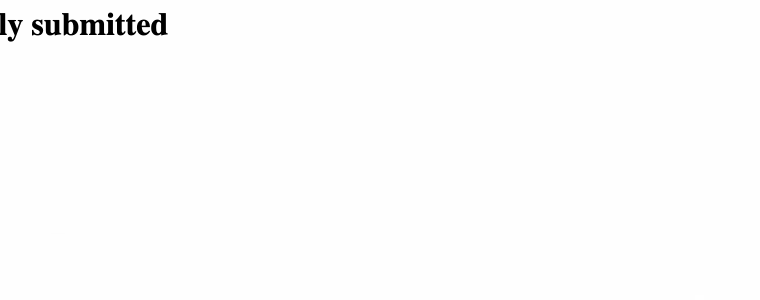
If an uploaded file contains an image renderable by the browser, that image is resized on the server and a thumbnail version is returned to the client. For other file types, a symbolic icon is returned.
Footnotes